Hey there, fellow data enthusiasts! Have you ever wondered how massive amounts of data can be stored efficiently, making it easily accessible for analysis? Well, let me introduce you to the superheroes of data storage: Parquet files!
Choosing the right file format is super important for making data processing and storage work effectively and scale smoothly. We have two popular file formats in the spotlight: Parquet and CSV. They both have their perks and find applications in various scenarios. So, in this article, we're going to break down how Parquet and CSV files work, compare their capabilities, and help you decide which one is best for your data based on its type and size.
We'll even throw in some visual examples of Parquet and CSV files to make things clearer. Plus, we'll cover how to load these files in Python and complete them with code examples and explanations.
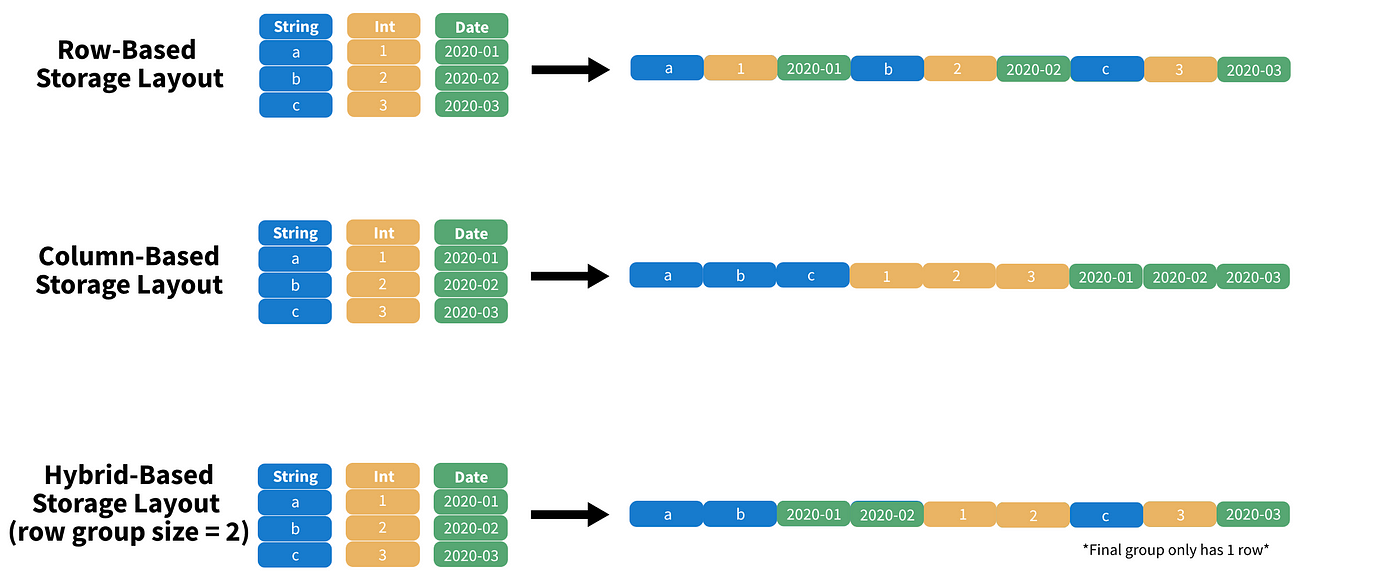
Parquet: It is a specialized data format optimized for efficient data storage and retrieval. It utilizes a columnar structure, allowing it to store data more compactly than CSV files. Consequently, Parquet files can be read and written with exceptional speed. Moreover, Parquet supports nested data structures, making it an excellent choice for storing complex data.
CSV: It is a popular row-based data format known for its simplicity in both reading and writing. Although CSV files may not match the storage efficiency of Parquet, they enjoy widespread support across various platforms. CSV files also offer the advantage of easy debugging, making them particularly suitable for development and testing purposes.
Which file format should you use?
The best file format to use depends on the specific needs of the application. If you need to store large amounts of data and need to read and write the data quickly, then Parquet is a good choice. If you need to support a wide range of data processing frameworks and need to be able to debug the data easily, then CSV is a good choice.
Visual Examples of Parquet and CSV Files
Here is a visual example of a Parquet file:
Here is a visual example of a CSV file:

Parquet file loading :

CSV file loading :
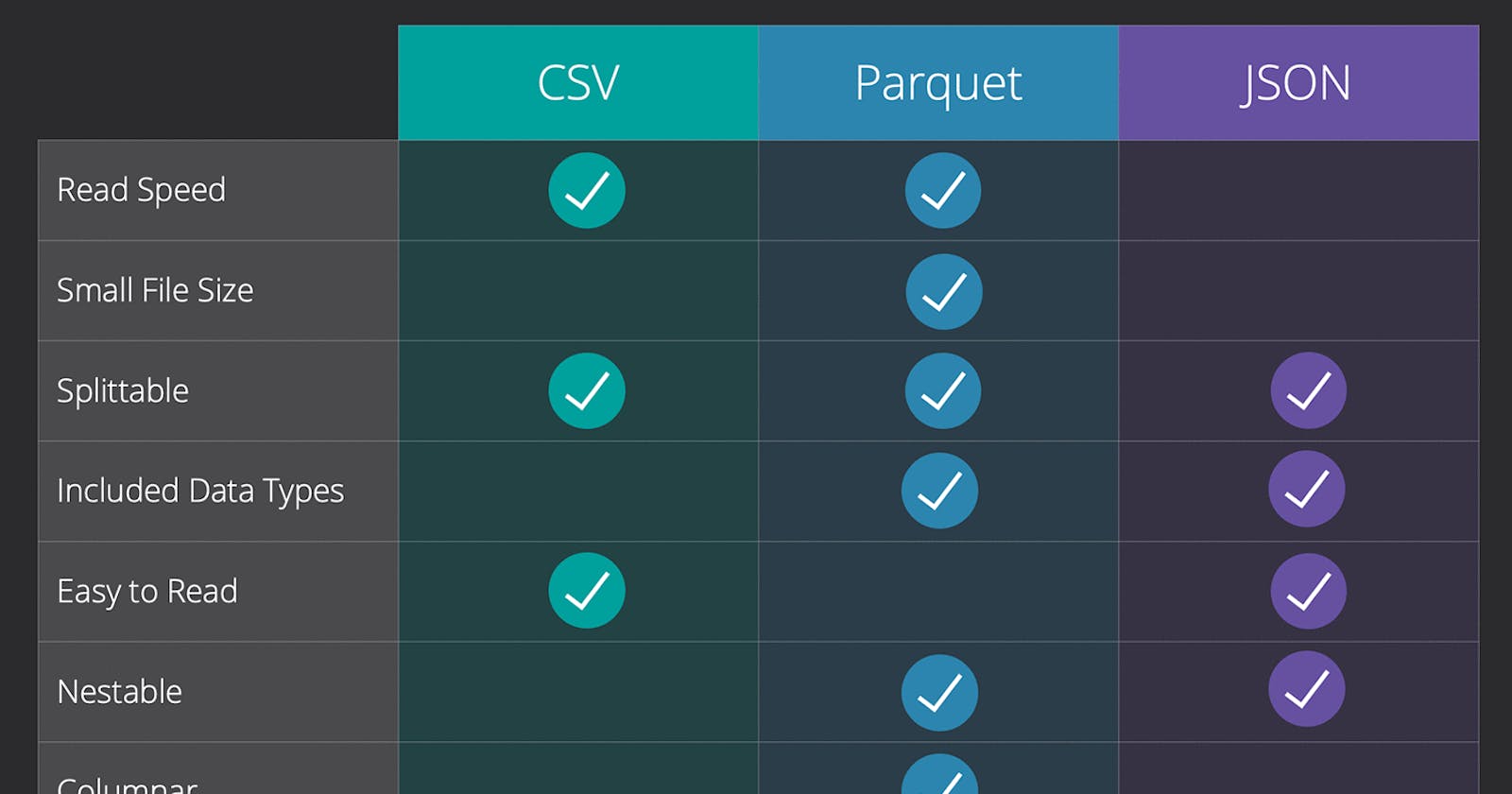
Pros and Cons at a Glance :
Parquet:
Pros:
Saves storage space
Faster queries
Supports schema evolution
Preserves data types and metadata
Supports complex data structures
Cons :
Requires specific tools
Less human-readable
Limited interoperability
CSV:
Pros:
Wide support
Human-readable
Simplicity
Familiarity
Cons:
Larger file size
Slower queries
No built-in schema evolution
Lacks support for complex data structures